

You should add variety to your activities.
#The hedonic treadmill refers to professional#
Variety is the spice in life: Healthy partnerships and professional development are key to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Activities that provide a strong sense or meaning to us are more resistant to the effects of hedonic adapt. Martin Seligman referred to these kinds of activities as “gratifications”–tasks that interest and challenge us and take us into flow. It lasts longer, which is the beauty of achievement. It can make you feel great and lift your mood, but it is also very short-lived and easy to forget. Choosing interventions that challenge but don’t overwhelm you is the best way to make sure you are able to get to the places you want and to grow. These interventions will help you get “into flow”. When you are looking for development opportunities, look for those that will challenge you but also keep your interest. Ask yourself “What really do in this situation?” Do I need another leadership course?” Do I need to take some time off, and appreciate my achievements before I embark on another challenging course? ”įind meaningful ways to make it meaningful. Recognize your shared humanity and accept that not everyone is perfect, whether you are a leader, mother or manager. You can invite kindness from both the fierce (which will tell you what you need/want to improve) and the tender (which allows you to be who you are and to accept where you are at the moment). To see what you have, take stock now and find out what’s going on. Self-compassion can help you discover what you truly need. There are three ways to transform your workout: In her quest for more comfort, security, and happiness in her leadership role she feels the need “to do more.” How can we stop this? Olivia is trapped in her own adaptation trap. Olivia believes that the only way to fix this is to join every program, in the hope of finding comfort.
This not only gives her a biased view of herself but also makes it difficult to develop a self-development plan that is both effective and tailored to her needs.
#The hedonic treadmill refers to full#
Part of Olivia’s challenge is that she has trouble seeing and accepting her full self–accomplishments included. She continues to look for new opportunities and says that the interventions she receives “don’t fill her void.” Olivia, a highly successful leader in her field is what she calls “professional development junkie”. I have seen many successful, educated and experienced clients experience the adaptation effect (or trap), on their professional development journeys. This adaptation effect is particularly important to professional development. To produce emotion, such as happiness or inspiration, the stimulus must be stronger than the previous stimulus.

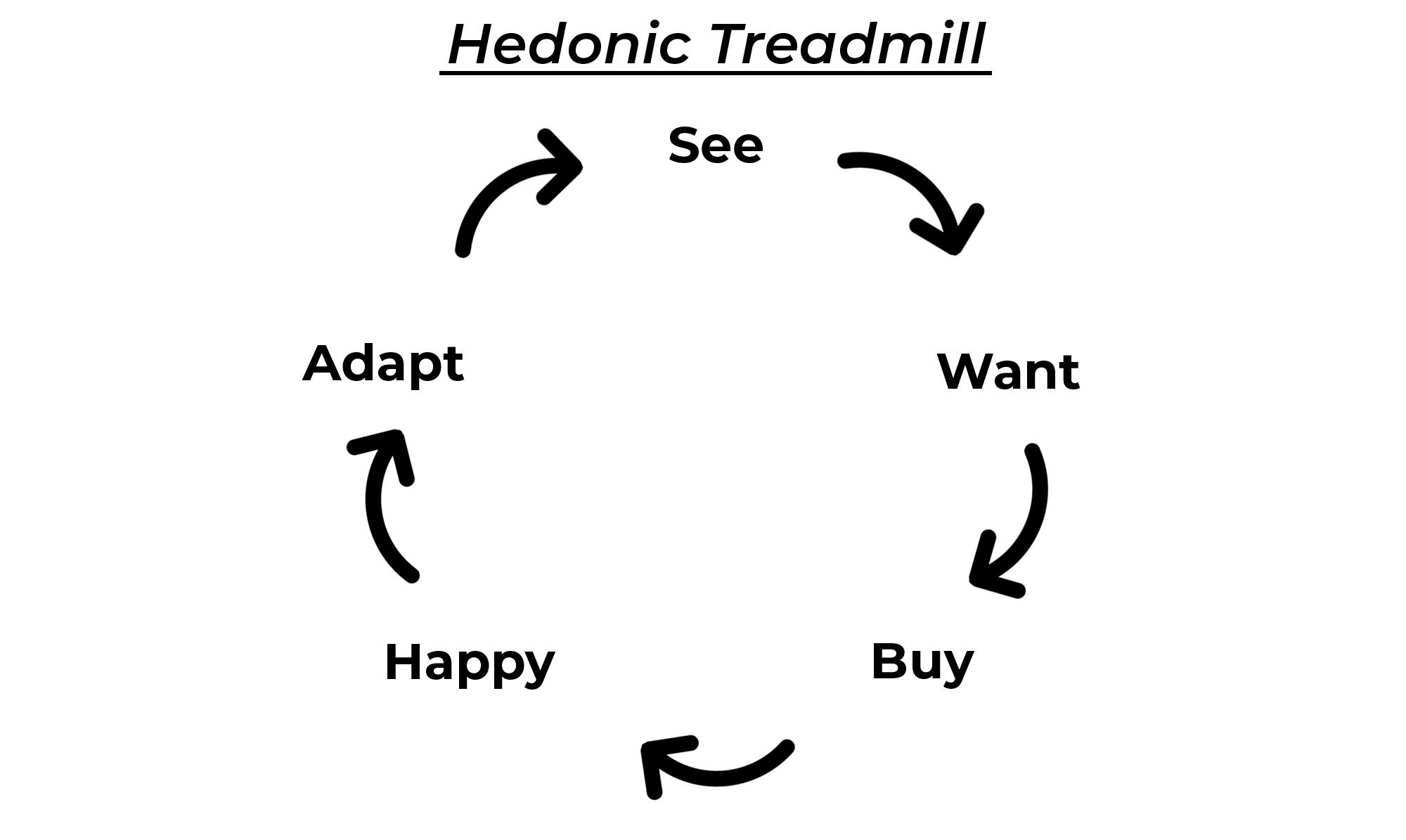
The treadmill, also known as hedonic adaption (or the treadmill), refers to the human tendency to quickly adjust to an emotional baseline and become less sensitive to new stimuli. They first used the term to describe people’s tendency toward a stable baseline level of happiness, regardless how their life changes. Brickman and Campbell in 1971 wrote “Hedonic Relativism and Planning the Good Society”. The term “hedonic treadmill” is a common expression of happiness. This is when they invest time and effort into improving themselves but don’t get the results or satisfaction they desire and feel they have to do more. But, I want to specifically focus on the fact that many people, including many of my female clients, can find themselves stuck on a professional growth hedonic treadmill. There are many factors that contribute to our different levels of satisfaction and pleasure in our work and ourselves: personality, imposter Syndrome, perfectionism and bias, just to name a few. The pleasure we take from professional development is often short-lived, which means that we return to the same level of happiness we had before we even took that course/workshop/seminar. This is what I have observed with my leadership coaching clients, who go through what I call the “hedonic treadmill” of professional development. Instead of feeling satisfied with their progress, they often feel worse than they did before starting their next piece of professional learning. Many people don’t feel the same about themselves after the initial joy passes. Do you remember the joy of completing training or earning a qualification? That good feeling can last for how long? Some people may not feel that good feeling for very long.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
